Incorporating low glycemic index foods into your diet can have numerous benefits. These foods tend to be more nutrient-dense, offering vitamins, minerals, and fiber that are often lacking in high glycemic index options. By focusing on whole, unprocessed foods, you not only enhance your overall nutrition but also promote better digestive health. For example, choosing brown rice over white rice or opting for sweet potatoes instead of regular potatoes can significantly impact your blood sugar response.
When planning meals, consider combining low glycemic index foods with healthy fats and proteins. This combination can further slow the absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a more stable blood sugar level. For instance, pairing oatmeal with nuts or yogurt can create a balanced meal that keeps you feeling fuller for longer while avoiding sharp spikes in blood glucose.
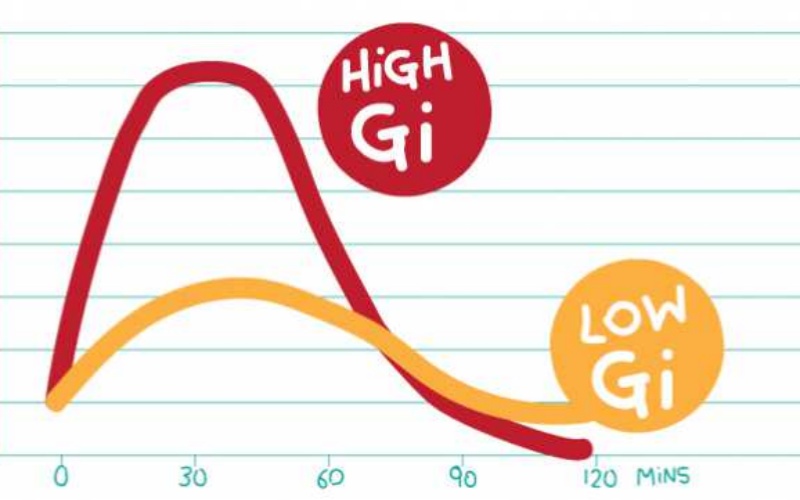
It is also essential to be mindful of portion sizes, as consuming large quantities of even low glycemic index foods can lead to increased blood sugar levels. Monitoring your overall carbohydrate intake, along with understanding the glycemic index of foods, can be a powerful strategy for maintaining optimal health.
For those looking to improve their diets, a practical approach is to gradually swap out high glycemic index foods for lower ones. Start by making small changes, such as replacing white bread with whole grain options or choosing fruits with a lower glycemic index, like berries and apples. These adjustments can lead to significant improvements in energy levels and overall well-being.

Understanding the glycemic index is an essential aspect of nutrition that can help individuals make informed choices. By prioritizing low glycemic index foods and adopting a balanced approach to eating, you can enhance your health and enjoy more stable energy throughout the day. This knowledge empowers you to take charge of your dietary habits and make lasting changes for a healthier lifestyle.




